
Telephone - 01628 483 752
Company Registration No.07690054
- Welcome
- News & Events
- About Us
- School Life
- Canteen & Catering
- Careers Programme
- Duke of Edinburgh’s Awards
- House System
- Library
- Lockers & Bicycle Racks
- One to One Laptop Scheme
- Parents’ Evenings
- Prefects: Sixth Form & Year 11
- Safeguarding
- School Nurse
- School Transport
- Student Support and SEN
- Teacher Training
- Transition to Year 7
- Uniform, Hair, Jewellery, Phones
- 6th Form
- Curriculum
- Parent & Carers
- Attendance Guide
- Bucks Family Information Service
- Bucks School Transport
- Communication & Catering
- Friends of Great Marlow School
- Information Evenings
- Gift Aid
- Letters Home
- Mental Health Support
- National Crime Agency
- Online Safety Resources
- Parent/Carer Services
- Progress Review Guides
- School Uniform Shops
- Special Educational Needs
- The Voice – School Newsletter
- Student Area
- Sport
- Gallery
Science Department
 ABOUT SCIENCE
ABOUT SCIENCE
The communication, research, reporting, and collaboration skills that science provides can produce a generation of individuals who are better prepared for all careers and who make greater contributions to society. Also, students who have a solid knowledge base in science will be more open to emerging technologies and ideas.
- Science at Great Marlow School
- Learning Ladders
- Wider Curriculum
- KS 3 Science
- KS 4 Science
- KS 5 Biology
- KS 5 Chemistry
- KS 5 Physics
- Careers in Science
 SCIENCE AT GREAT MARLOW
SCIENCE AT GREAT MARLOW
The Science Department, as one of the largest department in the school, has nine laboratories, as well as a number of associated ‘prep’ rooms, all contained in a purpose built block.
The department is continuously developing ideas and resources to make its lessons both informative and stimulating. Practical investigations are always popular with students and, at Great Marlow, we are fortunate in having a highly motivated technician team who prepare and organise equipment for practical lessons. Each laboratory in the science block carries a range of up to date scientific equipment, including media projectors, which enable the delivery of course material in a visually stimulating way. The department is also fortunate to have 30 wireless laptops.
| BIOLOGY KS3 & KS4 | BIOLOGY KS3 & KS4 TRILOGY | BIOLOGY KS5 | ||
 |
 |
 |
| CHEMISTRY KS3 & KS4 | CHEMISTRY KS3 & KS4 TRILOGY | CHEMISTRY KS5 | ||
 |
 |
 |
| PHYSICS KS3 & KS4 | PHYSICS KS3 & KS4 TRILOGY | PHYSICS KS5 | ||
 |
 |
 |
WIDER CURRICULUM
The Wider Curriculum allows students to take a further interest in their subjects and subject related material they study at school. The Wider Curriculum also enables parents and carers to actively engage with the opportunities offered by each department. Each PDF is hyperlinked, so when you click on them, the links will take you to areas where you may read, view, listen, visit and be creative.
| SCIENCE WIDER CURRICULUM KS3 | SCIENCE WIDER CURRICULUM KS4 | SCIENCE WIDER CURRICULUM KS5 | ||
 |
 |
 |
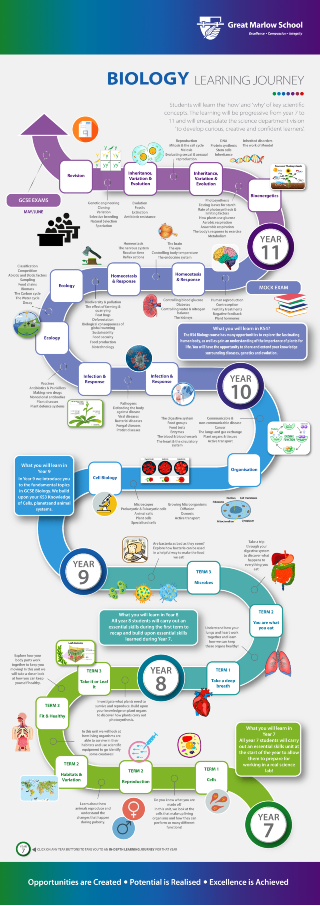
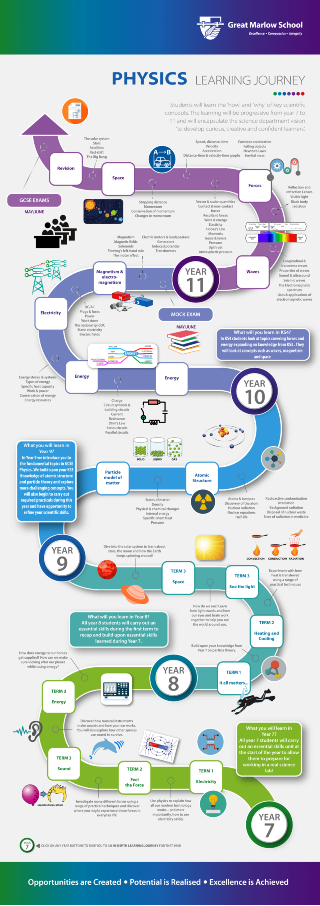
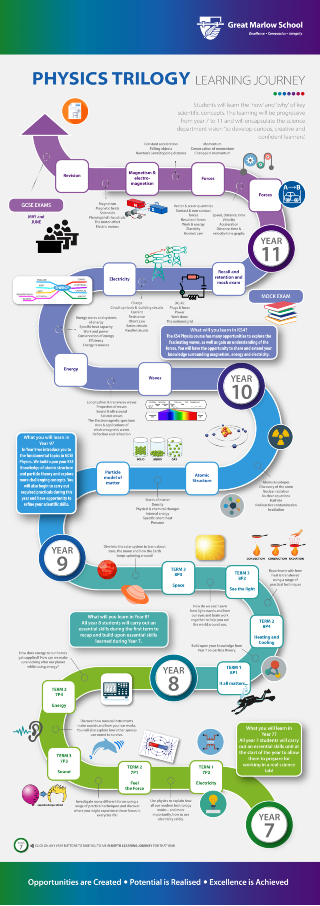
KEY STAGE 3 SCIENCE
In Years 7 and 8 students follow a spiral curriculum visiting core themes from each of the three sciences. They visit the same themes in Year 7 and Year 8 with increasing complexity. In Year 9 students are introduced to the GCSE course, focusing on the more complex elements of the core themes already studied. Married to the content, is the teaching of specific scientific skills to develop students’ understanding of the scientific process, experimental design, measurement, fair testing and repeatability.
The aim of the KS3 science curriculum is to give the students a solid foundation of scientific knowledge and understanding in order to prepare them for their KS4 courses, but more importantly, to ignite a passion and spark a curiosity in the subject. To this end science lessons encourage the students to ask questions, to take risks in their learning and, of course, to carry out practical work.
Assessment in KS3
Students complete a reflection (DEAL) sheet to self-assess their knowledge before the module begins and to assess their progress after the module has been taught. An assessment is completed at the end of every half term. Staff collate all the marks gathered to make an informed professional judgement about the progress of students. Progress report grades will be based on the results of the end of term assessments, student classwork and homework and student ATL.
Year 7
- Introduction to Science – What is a scientist? An introduction into scientific skills.
- The particulate nature of matter- What makes up a solid, liquid and gas and how they change in state.
- Atoms, elements and compounds- An introduction to this fundamental chemical principle.
- Acids and alkalis- An introduction to hazards and risks and the reactions of acids and alkalis.
- Motion and Forces- An introduction to Newton’s laws.
- Sound and the ear- An introduction to waves.
- Electricity- An introduction to simple circuits .
- Structure and function of living organisms- A study of cells and using microscopes.
- Reproduction- An introduction to reproduction in animals, the menstrual cycle, gestation and birth.
- Interactions and interdependencies- An investigation into food chains and food webs.
- Movement- A study of breathing, muscles and bones, diet and exercise.
- Energy – A project to look at the formation of fossil fuels, the impact of fossil fuels and alternative energy resources.
Year 8
- Essential skills- Investigating further the use of mathematical skills in Science, SI units and variables.
- The science of burning- An investigation into combustion and fire safety.
- The periodic table- A study of the development of the periodic table and investigating physical and chemical trends.
- Materials- A study of the structure of the Earth, rocks and plate tectonics.
- Heating and cooling- Investigating energy transfers in the form of conduction, convection and radiation.
- Matter- Applying particle theory to pressure, density, upthrust and drag.
- Waves- An investigation into the properties of light.
- Space Physics. An introduction to the concept of space.
- Structure and function of living organisms- An introduction to respiration.
- Diet and digestion- A study of balanced and unbalanced diets and an introduction to digestion.
- Microbiology – Applying knowledge of cells to microorganisms.
- Inheritance – A project to investigate how our genes control our characteristics.
Year 9 GCSE Science
The Science Department start students on their GCSE course in Year 9. The following modules will be taught to the Year 9s in 2019-2020. For more details of the course, see the details under the KS4 tab.
GCSE Biology Modules
-
- Cell biology
- Bioenergetics
- Ecology
GCSE Chemistry Modules
-
- Atomic structure and the Periodic Table
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
- The rate and extent of chemical change.
GCSE Physics Modules
-
- Particle model of matter
- Atomic structure
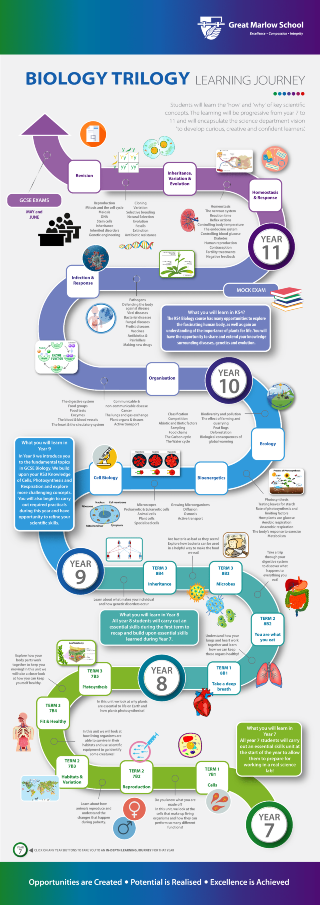
KEY STAGE 4 SCIENCE – AQA Science Trilogy (8464)
The Course
This course is like the old ‘double award’. Students will study the three sciences, but this is not a triple science course. This is a linear course, so all candidates sit final examinations at the end of Year 11. There are six exams (2 in each of the disciplines) and each one is 1 hour 15 minutes. Students will be given two examination grades. These will either be the same or consecutive figures based on student attainment in these exams. For example, students may have a 4-4 or 4-5 on their examination certificates. It is not possible to achieve two grades that are not the same or consecutive.
Students with a flair for science will study the AQA Science Trilogy course.
Non-Examination Assessments for the Science Trilogy (NEAs)
There are no NEAs. However, students have to carry out the 16 core AQA practicals. These will be conducted in class time. Questions about the practicals may be on the final examination paper, therefore attendance in lessons is vital. If students miss a required practical, they will not have the opportunity to do it again, but will instead, be directed to resources on Teams.
Year 10 GCSE Biology Modules
- Cell biology
- Organisation
- Biogenetics
- Ecology
Year 10 GCSE Chemistry Modules
- Atomic structure and the Period Tables
- Bonding structure and the property of matter
- Quantitative chemistry
- Chemical changes
- Energy changes
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
Year 10 GCSE Physics Modules
- Energy
- Electricity
- Particle model of matter
- Atomic structure
Year 11 GCSE Biology Modules
- Infection and response
- Homeostasis and response
- Inheritance, variation and evolution
Year 11 GCSE Chemistry Modules
- Quantitative chemistry
- Theatre and extent of chemical change
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical analysis
- Using resources
Year 11 Physics Modules
- Forces
- Waves
- Magnetism and electromagnetism
- Space
Examination Details
Each examination is 1 hour 15 minutes in duration. The six papers are each worth 70 marks (16.7%) of the final grade. There is a question mix of multiple choice, structured, closed short answers, and open response. At the end of Year 11, in GCSE Science Trilogy, students are awarded one grade (9 to 1).
KEY STAGE 4 SEPARATE SCIENCE – AQA Biology 8461, Chemistry 8462, Physics 8463.
The Course
This course has three distinct examinations for biology, chemistry and physics, it is assessed externally through written exams. As the course is linear, all candidates sit final examinations at the end of Year 11. There are six exams: two biology, two chemistry and two physics, each examination assesses knowledge and understanding of the subject: each examination is 1 hour 45 minutes duration. Students will be given an examination grade for each discipline. Students will either be entered for the Higher (9-4) or Foundation tier (5-1): no mixing of tiers permitted.
Non-Examination Assessments (NEAs)
There are no NEAs in the separate science course. However, students have to carry out the AQA required practicals. These will be conducted in class time. Questions based on the practicals may be on the final examination paper, therefore attendance in lessons is vital. If students miss a required practical, they will not have the opportunity to do it again, but will instead, be directed to resources on Teams.
Year 10 GCSE Biology Modules
- Cell biology
- Organisation
- Biogenetics
- Ecology
Year 10 GCSE Chemistry Modules
- Atomic structure and the Period Tables
- Bonding structure and the property of matter
- Quantitative chemistry
- Chemical changes
- Energy changes
- Chemistry of the atmosphere
- Using resources
Year 10 GCSE Physics Modules
- Energy
- Electricity
- Particle model of matter
- Atomic structure
Year 11 GCSE Biology Modules
- Infection and response
- Homeostasis and response
- Inheritance, variation and evolution
Year 11 GCSE Chemistry Modules
- Quantitative chemistry
- Theatre and extent of chemical change
- Organic chemistry
- Chemical analysis
- Using resources
Year 11 Physics Modules
- Forces
- Waves
- Magnetism and electromagnetism
- Space
Examination Details
Each examination is 1 hour 45 minutes in duration. The six papers are each worth 50% of each subjects’ grade. e.g. Chemistry Paper 1 is worth 50% and Chemistry Paper 2 is worth 50%. Each paper is worth 100 marks. There is a question mix of multiple choice, structured, closed short answers, and open response. At the end of Year 11, students are awarded a grade (9 to 1) in each of the science subjects.
Homework
Students will have two teachers for science, these teachers will alternate in the setting of homework. Homework will be set once a week and should take 45 minutes to complete.
Assessment
Students will complete an assessment each half term. These will assess understanding from all aspects of the GCSE Science course that has been studied to date. Therefore, each exam will assess content from previous years or terms work.
Resources
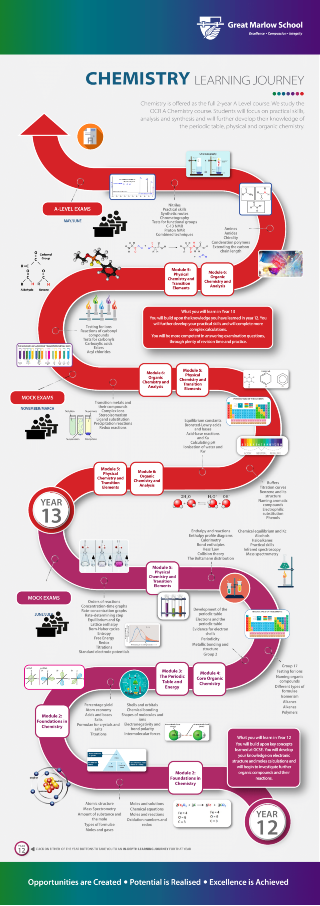
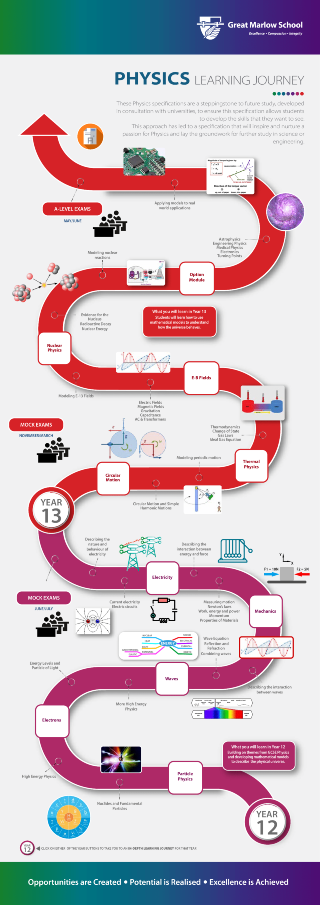
KEY STAGE 5 BIOLOGY 2017 REFORMED A-LEVEL
Biology allows you to ask questions about the world that we live in, and understand the living things that make it up, in greater detail. The skills that you develop during this course provide an excellent grounding for a wide variety of future degree courses and employment. Biology is an A-level that opens many different doors. It offers a diversity of opportunity leading to further studies in life science, medicine, environmental science or forensic science, through biological based employment such as biotechnology or the food industry.
The course offers students the opportunity to further develop their practical skills and to learn about the applications and implications of biology, the benefits and risks that research brings and the ways in which society uses biology to make decisions.
Entry Requirements
The qualification builds on the knowledge and practical skills students have gained in GCSE Separate Sciences or GCSE Combined Science.
Students are required to attain Grade 7 in all GCSE Biology or a 7-7 in GCSE Combined Science, to be assured of a place on the A-level science course. However, consideration will be given to students who achieved Grade 7-6 in GCSE Combined Science.
10% of the marks available in written examinations will be for assessment of mathematics (in the context of biology) at a Level 2 standard, or higher. Therefore, students with a Grade 7 or above in GCSE mathematics, as well as those studying A-level Mathematics, would be at an advantage.
Course Content
OCR Biology A-level is split into six modules: modules one to six, combined with the practical endorsement, constitute the full A-level. The modules can be summarised as:
-
-
- Module 1: Development of Practical Skills This module studied in Year 12 and Year 13 underpins the whole of the specification, and covers the practical skills that students should develop throughout the course. The practical skills in this module are assessed in the written examinations and (for A-level only) within the practical endorsement.
- Module 2: Foundations in Biology This module studied in Year 12 and Year 13 introduces students to the concepts required for all the other modules.
-
Modules studied in Year 12
-
-
- Modules 3: Exchange and Transport This module covers exchange surfaces, transport in animals and transport in plants.
- Module 4: Biodiversity, Evolution and Disease This module covers communicable diseases, disease prevention, the immune system, biodiversity, classification and evolution.
-
Modules studied in Year 13
-
-
- Modules 5: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy Covers communication, homeostasis, excretion as an example of homeostatic control, neuronal, hormonal communication, plant & animal responses, photosynthesis and respiration.
- Module 6: Genetics, Evolution and Ecosystems This module covers cellular control, patterns of inheritance manipulating genomes, cloning, biotechnology, ecosystems, populations and sustainability.
-
A-level Assessment
Paper 1: Biological Processes
-
-
- Examines content from modules 1, 2, 3 and 5
- Assessment: 2¼ hour written exam.
- Worth 100 marks – 37% of A-level mark.
-
Paper 2: Biological Diversity
-
-
- Examines content from modules 1, 2, 4 and 6
- Assessment: 2¼ hour written exam.
- Worth 100 marks – 37% of A-level mark.
-
Paper 3: Unified Biology
-
-
- Synoptic paper examining content from all modules 1 to 6
- Assessment: 1½ hour written exam.
- Worth 70 marks – 26% of A-level mark.
-
Non-Exam Assessment:
A portfolio of 12 practicals is assessed by the teacher as pass or fail and is separate to the overall grade.
The topics for the practicals are:
-
-
- Dissection
- Chromatography or electrophoresis
- Colorimeter or potometer
- Investigation into measurement of plant or animal responses
- Investigation using a data logger or computer modelling
- Microbiological techniques
- Microscopy
- Qualitative testing
- Rates of enzyme controlled reactions
- Research skills
- Sampling techniques
- Transport in and out of cells
-
The assessment criteria for the practicals are:
-
-
- the safe and correct use of a range of practical equipment and materials
- an ability to follow written instructions
- the organisational skills to keep appropriate records of experimental activities
- make and record observations/measurements
- present information and data in a scientific way
- use a wide range of experimental and practical instruments, equipment and techniques
-
KEY STAGE 5 CHEMISTRY 2017
Chemistry forms an increasingly important part of our everyday lives and this OCR Specification A course reflects this by providing understanding of core chemical concepts including the periodic table, the elements, physical chemistry, chemical synthesis, analytical techniques, organic chemistry and analysis.
Studying GCE Chemistry is full of practical experiences for students and these are embedded within each unit, reflecting its importance, as well as supporting the teaching and learning of the theory.
Entry Requirements
Students are required to attain Grade 7 in all GCSE Chemistry or a 7-7 in GCSE Combined Science, to be assured of a place on the A-level science course. However, consideration will be given to students who achieved Grade 7-6 in GCSE Combined Science.
Grade 6 or above in GCSE Mathematics is also required.
The aims of the course are to develop:
-
-
- students’ interest in and enthusiasm for chemistry, including developing a potential interest in further study and a career in chemistry
- an appreciation of how society makes decisions about current scientific issues
- a deeper understanding of the skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works
- essential knowledge and understanding of different areas of the subject and how they relate to each other
-
Students may wish to include chemistry as part of a broad range of subjects or include a package focusing on the sciences.
Chemistry is a fascinating, challenging and well respected subject at A-level, the study of which can provide an opening to a variety of science-related careers or vocational courses at higher level including university.
The course is structured to enable completion of the A-level course, which is designed to be completed over two years. There is an allocation of eight hours of teaching each fortnight.
Students will be provided with the details to purchase appropriate textbooks. The school’s website does provide additional learning support in chemistry including the full OCR A in Chemistry e-spec.
A-level Units
-
-
- Paper 1 – Periodic Table, Elements and Physical Chemistry
- Paper 2 – Synthesis and Analytical Techniques
- Paper 3 – Unified Chemistry
- Non-Exam Assessment – Practical Endorsement for Chemistry
-
A-level Assessment
-
-
- Papers 1, 2 and 3 are assessed at the end of Year 13 with terminal written papers.
- The non-examination assessment is assessed throughout the year for the A2 course.
-
KEY STAGE 5 PHYSICS 2017
The aim of the course is to demonstrate the importance of physics as a human endeavour that interacts with social, philosophical, economic and industrial matters. Students will develop essential knowledge and understanding of physics so that they can utilise the experience in the everyday world. Students will develop experimental skills and be able to relate theory to experimentation.
Successful completion of this course will allow candidates to apply for a number of further education courses: BSc Physics, BSc in an engineering discipline, which may include medical physics, electrical engineering and mechanical engineering and many other courses.
Entry Requirements
Students are required to attain Grade 7 in all GCSE Physics or a 7-7 in GCSE Combined Science, to be assured of a place on the A-level science course. However, consideration will be given to students who achieved Grade 7-6 in GCSE Combined Science.
Grade 6 or above in GCSE Mathematics is also required.
Candidates follow the AQA course which requires 8 hours of study per fortnight, and 2 hours of homework.
Subjects in Year 12
-
-
- Measurements and their Errors This unit will give you a working knowledge of the fundamental base units and measurements. At the same time showing that practical work is underpinned by an awareness of the nature of measurement errors and of their numerical treatment.
- Particles and Radiation This unit starts with the simple model of the atom and finishes with the interaction of quarks and anti-quarks.
- Waves This unit develops knowledge of the characteristics, properties and application of waves.
- Mechanics and Materials This unit considers the ideas of forces, energy and momentum in terms of material properties.
- Electricity This unit looks at the basics of electricity including resistance and resistivity.
-
Subjects in Year 13
-
-
- Further Mechanics and Thermal Physics This unit covers circular motion and simple harmonic motion; it also covers the thermal properties of materials.
- Fields This unit covers the ideas of gravitational, electrostatic and magnetic field theory.
- Nuclear Physics This unit looks at the properties of the nucleus and relates it to the production of nuclear power and it considers the impact this has on society.
-
A final unit will be chosen by the group from the following options; astrophysics, medical physics, engineering physics, turning points in physics and electronics.
Practical lessons will support all topics taught throughout the course, the knowledge and skills gained through these lessons will be assessed within the A-level exam papers.
Assessment
Three written exams; each will include objective questions and written answers. All papers are 2 hours in length. Papers 1 and 2 are worth 34% each and Paper 3 is worth 32% of the total A-level mark.
Careers in Biology |
||
| Dentist | Nurse | Nutritionist |
| Dietician | Paramedic | Pharmacologist |
| Doctor | Medical Research | Laboratory Technician |
| Microbiology | Biotechnology | Sports Scientist |
| Sports Coach | Health / Lifestyle Coach | Physician |
| Scientific Sales | Brewery production | Greenhouse Curator |
| Garden Curator | Botanical Technician | Environmental Consultant |
| Environmental Technician | Nutritionist | Horticulturist |
| Food Inspector | Agricultural or Wildlife fields | Veterinarian |
Careers in Chemistry |
||
| Analytical Chemist | Agriculturalist | Bio-technologist |
| Chemical Education | Chemical Engineer | Chemical Sales |
| Chemical Technologist | Biochemist | Food and Flavour Chemist |
| Forensic Chemist | Geochemist | Environmental Chemist |
| Materials Scientist | Medicinal Chemist | Organic Chemist |
| Science Writing | Textile Chemist | Inorganic Chemist |
| Water Chemist |
Careers in Physics |
||
| Physicist | Astrophysicist | Aeronautical Engineer |
| Automotive Engineer | Medical Physicist | Research Scientist |
| Laboratory Technician | Nuclear Engineer | Software Engineer |
| Scientific Journalist | Optometrist | Forensic Scientist |
| Energy Explorer | Patent Attorney | Satellite Data Analyst |
| Business Manager | Physics Consultant | Clinical Psychologist |
| Satellite Data Analyst | Business Manager | Physics Consultant |
| Clinical Psychologist | Telecommunications Engineer | Air Traffic Controller |
| Teaching | Technical Illustrator | The Armed Forces |